Difference Between Tax Planning and Tax Management

The difference between tax planning and tax management is a common topic that confuses many people, especially when filing taxes or planning finances for the future. While both focus on handling taxes better, they are not the same. Each serves a different purpose and works at a different stage of your financial journey.
In this informative blog, we will clearly explain what tax planning and tax management mean, how they work, and why both are important. By the end, you will fully understand the tax planning and tax management differences and how to use them wisely in your daily life.
What Is Tax Planning?
Tax planning is the process of legally reducing your tax liability before it arises. It focuses on future income and expenses. The main goal is to save taxes by making wise financial choices in advance.
Tax planning helps you decide where to invest, how to claim deductions, and how to structure income so that you pay the least tax possible within the law.
Key Features of Tax Planning
- Done before the financial year ends.
- Focuses on long-term savings and investments.
- Uses tax deductions, exemptions, and rebates.
- Helps grow wealth while saving tax.
- Requires proper knowledge and planning.
Examples of Tax Planning
- Investing in tax-saving instruments like PPF or ELSS.
- Claiming deductions under Sections like 80C or 80D.
- Planning capital gains to reduce tax impact.
- Choosing the proper salary structure.
In short, tax planning is proactive. You plan early so there are no surprises later.
What Is Tax Management?
Tax management is the process of handling taxes after income is earned. It focuses on compliance and timely actions rather than future planning.
The main aim of tax management is to make sure you follow tax laws correctly and avoid penalties or interest.
Key Features of Tax Management
- Done throughout and after the financial year.
- Focuses on tax filing and compliance.
- Includes payment of taxes on time.
- Helps avoid fines and legal trouble.
- Requires proper records and documents.
Examples of Tax Management
- Filing income tax returns on time.
- Paying advance tax and self-assessment tax.
- Keeping records of income and expenses.
- Responding to tax notices.
Simply put, tax management is reactive. It deals with taxes after they occur.
Difference Between Tax Planning and Tax Management
Understanding the difference between tax planning and tax management becomes easier when you compare them side by side. Both are important, but their roles are different.
Meaning and Purpose
- Tax planning focuses on reducing tax liability legally.
- Tax management focuses on meeting tax obligations.
Timing
- Tax planning is done before income is earned.
- Tax management is done after income is earned.
Nature
- Tax planning is preventive.
- Tax management is corrective.
Main Objective
- Tax planning aims to save tax and build wealth.
- Tax management aims to avoid penalties and ensure compliance.
Scope
- Tax planning includes investments and financial decisions.
- Tax management includes filing returns and paying taxes.
This precise tax planning and tax management difference shows why both are needed for healthy finances.
Tax Planning vs Tax Management: A Simple Comparison Table
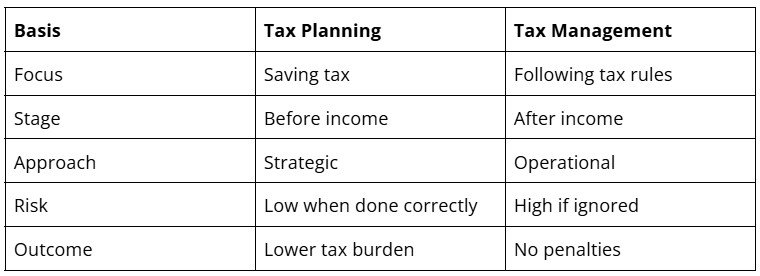
This tax planning vs tax management comparison highlights how one prepares you and the other protects you.
Benefits of Tax Planning
- Reduces overall tax burden.
- Improves long-term savings.
- Supports goal-based investing.
- Brings financial clarity.
Benefits of Tax Management
- Avoids late fees and interest.
- Ensures legal compliance.
- Keeps financial records clean.
- Reduces stress during tax season.
When combined, tax planning and tax management help you stay financially secure and stress-free.
Common Mistakes People Make
Even with a good income, many people struggle to manage their taxes. Here are some common mistakes.
Delaying Tax Planning
Waiting until the last month of the financial year limits your options. Good tax planning needs time.
Ignoring Tax Management
Missing deadlines or filing incorrect returns can lead to penalties, even if your tax planning is perfect.
Mixing Both Concepts
Many people assume investing once a year is enough. But tax planning and tax management are ongoing processes.
Avoiding these mistakes can save money and prevent trouble.
Choosing Fixed Deposits Instead of Debt Mutual Funds (Especially Post-Retirement)
Many retirees prefer Fixed Deposits (FDs) because they feel safe and familiar with them. However, large FD holdings can create tax inefficiencies.
Here’s why:
- Interest from FDs is fully taxable every year.
- If the interest amount is high, you may need to pay advance tax quarterly.
- This increases compliance burden and may lead to penalties if missed.
On the other hand, debt mutual funds (when aligned with tax rules and financial goals) may offer better tax efficiency and greater cash flow flexibility.
For example, a retiree with ₹50 lakhs in FDs earning 7% interest will earn ₹3.5 lakhs annually. This interest is fully taxable and may require advance tax payments in installments. Poor planning can result in penalties for underpayment.
The mistake is not evaluating tax impact before investing.
Delaying Tax Planning Until Year-End
Waiting until March to invest under Section 80C or 80D reduces flexibility. You may end up choosing unsuitable investments just to save tax, instead of aligning them with your financial goals. Good tax planning should start at the beginning of the financial year.
Common Tax Management Mistakes
Not Declaring Foreign Stock Holdings in Income Tax Returns
With global investing becoming popular, many individuals now hold:
- US stocks
- Foreign ETFs
- Shares through global brokerage platforms
However, many taxpayers forget that foreign assets must be disclosed in Schedule FA (Foreign Assets) while filing Income Tax Returns in India.
Even if:
- You made no profit
- You did not sell the stocks
- The value is small
Disclosure is mandatory for residents. Failure to report foreign holdings can lead to serious consequences under the Black Money Act, including heavy penalties. Tax management is not just about paying taxes. It is also about accurate disclosure.
Not Paying Advance Tax Quarterly
Advance tax applies if your total tax liability exceeds ₹10,000 in a financial year.
This is common for:
- Freelancers
- Business owners
- Investors earn capital gains
- Individuals earning high FD interest
Advance tax must be paid in four installments:
- June
- September
- December
- March
If you skip these and pay everything at the end, interest under Sections 234B and 234C may apply.
Example:
Suppose your tax liability is ₹1,20,000 for the year. If you pay nothing during the year and settle it in March, you may still have to pay interest for the delay in advance tax payments. This increases your total outflow unnecessarily. Good tax management means tracking income throughout the year and paying taxes on time.
Ignoring Notices or Filing Returns Incorrectly
Even small errors in filing, such as mismatches in Form 26AS or AIS, or incorrect income reporting, can trigger notices. Responding late can escalate the issue. Proper documentation and timely response are critical parts of tax management.
How to Do Tax Planning and Tax Management Effectively
Managing taxes becomes easier when you follow a structured approach.
Steps for Better Tax Planning
- Start planning at the beginning of the year.
- Understand your income and expenses.
- Choose tax-saving investments wisely.
- Review your plan regularly.
Steps for Better Tax Management
- Keep all income proofs and bills.
- Pay advance tax if required.
- File returns before the deadline.
- Seek help if you get a tax notice.
Following these steps ensures smooth tax planning and tax management every year.
Who Needs Professional Help?
While basic taxes can be managed on your own, complex finances need expert guidance.
You may need help if you have:
- Multiple income sources.
- Business or freelance income.
- High-value investments.
- Long-term financial goals.
Professional support ensures your tax planning and tax management difference is handled correctly.
How FinAtoZ Helps With Smart Tax Decisions
FinAtoZ is a SEBI-registered financial planner in India that helps individuals make better financial decisions with confidence.
What FinAtoZ Does
- Plan Your Goals: Creates a personalized financial plan for your life goals.
- Invest Smartly: Manages investments based on your risk profile and goals.
- Track and Re-balance: Regularly tracks and adjusts your portfolio.
With expert guidance, FinAtoZ ensures your tax planning aligns with your long-term wealth goals while supporting smooth tax management.
You can explore real customer experiences here!
In Closing
The difference between tax planning and tax management lies in timing, purpose, and approach. One helps you save tax in advance, while the other ensures you meet your tax duties on time.
To stay financially healthy, you should not choose between them. Instead, use tax planning and tax management together. Plan early, manage well, and seek expert help when needed.
When done right, taxes stop being a burden and become a part of smart financial living.
To know more, explore the FinAtoZ expert blog section!
FAQs on the Difference Between Tax Planning and Tax Management
What is the main difference between tax planning and tax management?
The main difference between tax planning and tax management is timing and purpose. Tax planning focuses on saving tax before income is earned by making wise financial decisions. Tax management focuses on handling taxes after income is earned by filing returns and paying taxes on time.
Is tax planning legal in India?
Yes, tax planning is completely legal when done within the rules set by tax laws. It uses approved deductions, exemptions, and investments to reduce tax liability. It is different from tax evasion, which is illegal.
Can tax management be done without tax planning?
Yes, tax management can be done without tax planning, but it may lead to higher tax payments. Without planning, you may miss out on tax-saving opportunities and end up paying more tax than needed.
Why are tax planning and tax management both important?
Tax planning and tax management are vital because one helps you save money, and the other helps you stay compliant. Together, tax planning and tax management reduce financial stress, prevent penalties, and support better long-term financial decisions.
Who should focus more on tax planning and tax management?
Anyone who earns income should focus on tax planning and tax management. It includes salaried employees, freelancers, business owners, and investors. The more complex your income, the more critical proper planning and management become.
Get Expert Financial Advice
Book an introductory call with our Certified Financial Planner to explore how we can help you achieve your financial goals.
Book Your Appointment
